

 |
Yoshitaka Kimura |
| Title | Professor Emeritus, MD., PH.D. |
| Institution | Tohoku University |
| Department | Graduate School of Medicine |
| Adress | Tohoku University Hospital, |
| 1-1 Seiryo-machi, Aoba-ku |

Study of fetal electrocardiography (fECG): the interface between medical science and frontier information engineering
1. Background: the difficulties of extracting fECG via the maternal abdominal wall
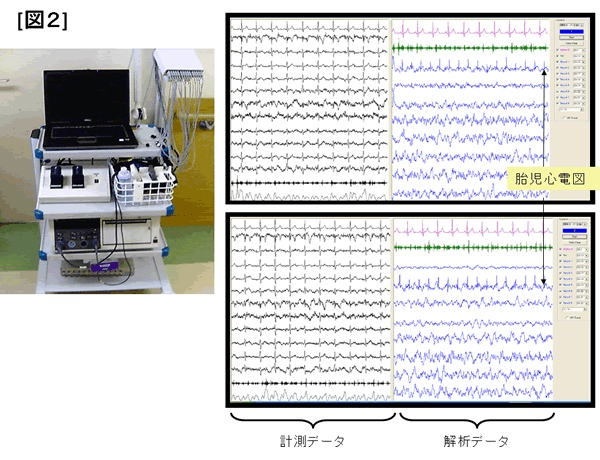
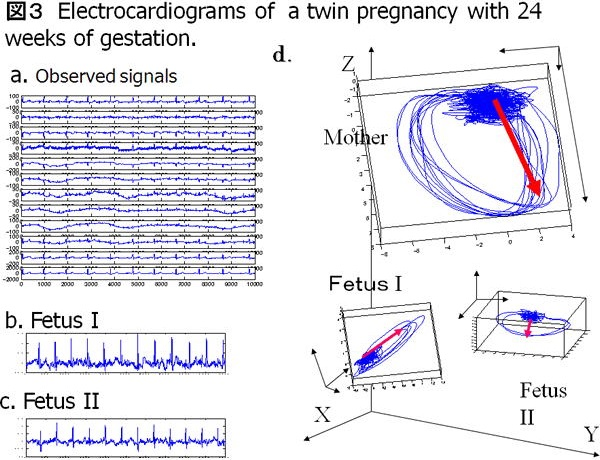
One ideal way to check the fetal status is by measuring fetal ECG signals. This significantly allows the examination of the state of the fetus during gestation. The most ideal way to measure it is to place electrodes on the maternal abdomen, which used to be considered dysfunctional. The ECG signal voltage of a fetus (5 to 20 microvolts) is approximately 1 in 200 to 1 in 50 of the maternal signal (approximately 1000 microvolts). In comparison to that, the EMG signals of the maternal abdomen range from approximately 30 to 100 microvolts and the voltage from nearby power supply humming ranges from 20 to 50 microvolts. The voltage of fetal ECG signals being significantly low, made their recording previously impossible.
2. Our research: new measurement theories and advanced equipment
We formulated a new information theory to enable the extraction of signals from electronic noise. This theory is derived from the "Independent component analysis" methods which identifies signals based on the probabilistic structure of information. The new theory stabilizes the analysis, and improves the quality of measurement. In addition, to eliminate the inconvenient use of bio-amplifiers which do not actually deal with microvolt measurement, we have developed an electrode with special filter functions.
3. Future progress
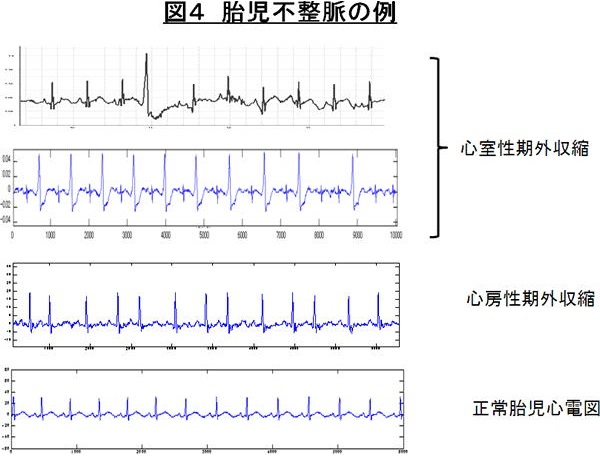
At present, our goal is to create an intelligent electrode with an independent filtering function to determine both the status of the fetus and the mother. This will enable ambulatory monitoring in the hospital and at home prior to delivery. Some picture use and in everyday life, the state grasp of the fetus, such as operation of the car and (ubiquitous fetal maternal monitoring system development). In addition, (unrestrained maternal fetal monitoring system development) as well as promoting research for a long time monitoring for the development by leaps and bounds the study of fetal heart rate variability that has been done previously. In addition, the successful state measurement of in utero of using the mouse fetal electrocardiogram for the first time in the world, we are studying the relationship between the change in heart rate and changes in the gene network, such as fetal hypoxia at the time as this application.
【 International development of Fetal ECG research 】
